In today’s digital world, data breaches are no longer a matter of if they happen, but when. The Dark Web, an encrypted and hidden part of the internet, has become a marketplace for stolen identities, leaked company data, and compromised login credentials, including banking and financial accounts.
With thousands of stolen records being traded every day for profit or criminal use, it’s increasingly likely that individuals and businesses alike will be affected by a data breach at some point.
This is where dark web monitoring comes into play, helping people and organizations track underground forums and marketplaces to identify whether their sensitive information has been stolen, misused, or put up for sale.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll gain a clear understanding of what dark web monitoring is, how it works, why it offers legitimate value, and who can benefit most from using it.
What is Dark Web Monitoring
Dark web monitoring is a proactive cybersecurity product that constantly monitors the Dark Web (the underground web containing sites not visible in regular browsing) for your information or your company’s information. To fully understand the environment it monitors, it helps to first grasp what the dark web is and how it functions. Think of it as having a dedicated guard in the depths of the darkness.
The primary reason for scanning hidden forums and marketplaces is for the early discovery of information that a cybercriminal has obtained. When attackers compromise your computer system, it can take months or even years before you or the company realizes the information was stolen and notifies those affected.
During that time, attackers could consolidate, sell, resell, and spread the information across the dark web marketplace. It identifies when your information hits the marketplace and allows you the opportunity to mitigate the damage by changing your password or enabling multi-factor authentication prior to the cybercriminal being able to commit identity theft, financial fraud, or corporate espionage.
Although underground intelligence gathering does not prevent the theft of data, it does provide an early warning system that can limit the impact of that loss.
Dark Web Monitoring: How It Works
The Dark Web Monitoring system combines sophisticated automation and consumer engagement to provide the end user with real-time reporting of suspicious activity related to their personal information. The service continuously automates monitoring, engages personally, and sends alerts about the information being tracked.
Automated Scanning Technology
At its core, dark web scanning is an automated process. A number of specialized bots and web crawlers exist that automatically search the dark web (generally the Tor network) for the types of content that fit the description of dark web content, including:
- Criminal marketplaces (which are where individuals can buy Stolen Information, i.e., Credit Card Dumps and Leaked Databases).
- Hacker forums (places where hackers can discuss hacking and share data)
- Paste sites (like Pastebin), where hackers generally list large amounts of stolen information.
- Private chat channels (on platforms such as Telegram and IRC that require sophisticated levels of access).
For those seeking to understand the structure and types of sites that constitute this hidden ecosystem, our guide to the best dark web sites provides a detailed overview of these platforms and their functions.
The automated scanning technology combs through millions of data points across dark web forums, marketplaces, and chat channels, searching for matches to the sensitive information on your personal or company watchlist.
Human Analyst Verification
Automated scanner raw data results are filled with either inconclusive False-Positive findings or simply noise. One of the major differentiators for a quality service is the existence of an additional layer of Human Power (Human Intelligence).
Human analysts review every potential match. They must evaluate the context: Is this an active, current database from a verifiable breach, or a dormant archive? More importantly, what is the threat actor’s intent? Like, are they actively selling this data, or just discussing it in a forum?
Human analyst verification ultimately allows security advisories to be both accurate and actionable so that alert fatigue (or a surplus of warnings that mean very little) does not set in.
Real-Time Alerting Systems
When a human analyst has verified that a vulnerability is valid, the system creates an alert for the customer. The quality of this warning is key. A good alert doesn’t just say “your data was found.” It provides essential context:
- What was found: For example, “The email address, [email protected], and the associated password hashes.”
- Where it was found: For example, “In the data dump posted on the hacker forum titled ‘XSS’ on March 7, 2024.”
- Source of the breach: For example, “Linked to the Database Breach (‘ExampleStream’) that occurred in 2023.”
- Recommended action: For example, “Change Your Password on ExampleStream and all other sites where you reuse it. Enable 2-Step Verification.”)
Breach notifications are sent to customers via their dashboard, email, and/or SMS, allowing the customer to respond quickly.
Key Benefits of Dark Web Monitoring
Implementing dark web monitoring provides several strategic advantages beyond simple breach notification:
Detect Breach Alert
This is the most direct benefit. It provides the earliest possible warning that your data has been compromised, often long before the breached organization informs you. This time advantage is critical for containing damage.
Proactive Threat Intelligence
For businesses, dark web monitoring turns captured data into actionable intelligence, helping them detect if employees discuss company records over unsecured channels or if attackers plan to target the organization.
The information received from underground intelligence gathering enables security teams to change their approach from a reactive stance to a proactive one.
Stay Compliant
Many regulations (such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA) have stringent requirements regarding breach disclosure and how to protect your customers’ personal information. Creating a dark web monitoring program is one way to demonstrate you have taken reasonable measures to ensure the safety of your employees’ and customers’ information. It provides an audit trail showing active efforts to discover breaches.
Customer Trust Protection
With dark web monitoring, organizations can establish a trusting relationship with their customers. For many businesses, quickly and knowledgeably responding to a security breach is an incredible indicator of trust.
Notifying customers of data being located on the dark web prior to their experience with fraud and informing them of clear remediation will lead to customer loyalty, as well as help the business protect its reputation.
Is Scanning Hidden Markets and Forums Legitimate?

Although parts of the dark web can be used for legitimate privacy purposes, it has become a thriving marketplace for stolen identities, leaked company data, and compromised login credentials, including banking and financial accounts.
Because of its relationship with a shady side of the internet, there is a good reason to be concerned when determining whether or not the monitoring service is legitimate:
Legal Framework
Most, if not all, legitimate dark web monitoring services work within the law and use the same tools as journalists and researchers to locate publicly available information on the dark web, often using data that has already been compromised and subsequently shared online. The legality of underground intelligence gathering services is in monitoring, not hacking.
Scope and Limitations
To properly validate the legality of any dark net monitoring service, you must have a complete understanding of both the scope and limitations of the darknet monitoring service. Most dark web monitoring services cannot:
- Stop the original data breach
- Get rid of your personal or payment information from the dark web (once published, it will likely be copied multiple times and remain available forever).
- Search every possible space on the dark web (a majority of activity takes place in hidden or invitation-only areas).
Therefore, legitimate underground intelligence gathering services will typically be honest and upfront about the limits of their monitoring capabilities.
Another Layer of Security
When viewed correctly—as an intelligence and early-warning layer—it is a legitimate and valuable component of a defense-in-depth security strategy. It is not a silver bullet but a specialized tool that complements others like firewalls, antivirus software, and employee training.
Categories of Dark Web Monitoring Services
A dark web monitoring solution can vary from a simple consumer alert service to a complex enterprise platform, each designed for different needs.
Enterprise Monitoring Platforms
Services such as Digital Shadows and ZeroFox offer large companies complete systems that include constant, deep-level dark web monitoring of all types, not just data leaks, but also for false brand representations, threats to executives, and physical security threats.
They come with robust analytics capabilities, integration with SIEM (security information and event management) systems, and dedicated threat intelligence teams.
Small Business Solutions
For smaller businesses, there are affordable, streamlined dark web breach detection tools like Have I Been Pwned for Business and Breach Alarm, which are aimed at providing smaller-scale solutions to help with monitoring a company’s domain names and vendor risks, as well as leaked credentials. These tools provide easier-to-use dashboards and clearer alerting capabilities than enterprise monitoring platforms.
Consumer Monitoring Services
The majority of deep web monitoring services available are intended for individuals and are usually included in identity theft protection programs (e.g., Experian IdentityWorks, LifeLock) or premium password managers (such as NordPass or Proton Pass).
These services monitor a limited number of email addresses and personal information, providing users with a basic understanding of any breaches that might have occurred, along with information on how to prevent similar problems in the future. They are a good entry point for individual protection.
Dark Web Monitoring for Businesses

Businesses must not simply purchase monitoring services but develop a long-term approach to the implementation of those services:
Strategizing Implementation
Begin by identifying the types of data you wish to monitor. What do you consider your most critical assets? This typically includes:
- All corporate email domains.
- Executive and key employee personal data.
- Key intellectual property keywords.
- Customer database samples (with consideration for privacy laws).
- Vendor and partner domains could be a backdoor into your systems.
Integration with Security Operations
For monitoring to provide meaningful value to an organization, alerts from monitoring services must be integrated into the organization’s established security processes, such as the organization’s SOC (security operations center) ticketing system and/or SIEM (security information and event management) tools.
Establish clear playbooks: What does the IT team do when an employee’s corporate credential is found? What does communications do if customer data is leaked? Automation here is key to a fast response.
Training and Awareness of Your Staff
Monitoring is not just for the IT department. HR should understand the risks of employee data leaks. Finance should be aware of executive impersonation scams. General staff training should include guidance on what to do if they receive a personal dark web warning related to their work email.
Measuring Success
Metrics are crucial. Track:
- Time to detection: How long from data appearing to your alert?
- Time to remediation: How long to contain the threat (e.g., password reset).
- Incidents prevented: Estimates of fraud or attacks thwarted by early action.
- Reduction in credential-based attacks: Measured through login attempt logs.
What Kind of Your Data is on the Dark Web?
The range of personal and corporate data traded is vast and constantly evolving:
Types of Information Dark Web Monitors Scan
- Personally identifiable information (PII): Identity theft starts with PII. Examples are full name, address, date of birth, SSN (Social Security Number), and passport info. Criminals often bundle this data into “full” packs and sell them for a premium.
- Financial credentials: Direct lines to money. Examples are credit/debit card numbers (including CVV and expiration date), bank account credentials, and PayPal account credentials. Cryptocurrency wallet keys and exchange account credentials are also very expensive on the dark web.
- Compromised credentials: The most common find. Hackers aggregate billions of username/email and password combinations from thousands of past breaches into massive lists, then use bots to try the same logins on hundreds of websites in “credential stuffing” attacks.
- Corporate data: A growing category. Includes internal employee directories, proprietary source code, confidential business plans, merger documents, and sensitive email archives. Competitors or nation-state actors often seek this.
- Healthcare records: Extremely valuable on the dark web. Attackers can use medical records, which contain vast amounts of PII, to claim fraudulent insurance reimbursements or obtain illegal prescriptions. A medical record alone could sell for as much as ten times a simple credit card number.
What Types of Risks Does Dark Web Monitoring Expose?
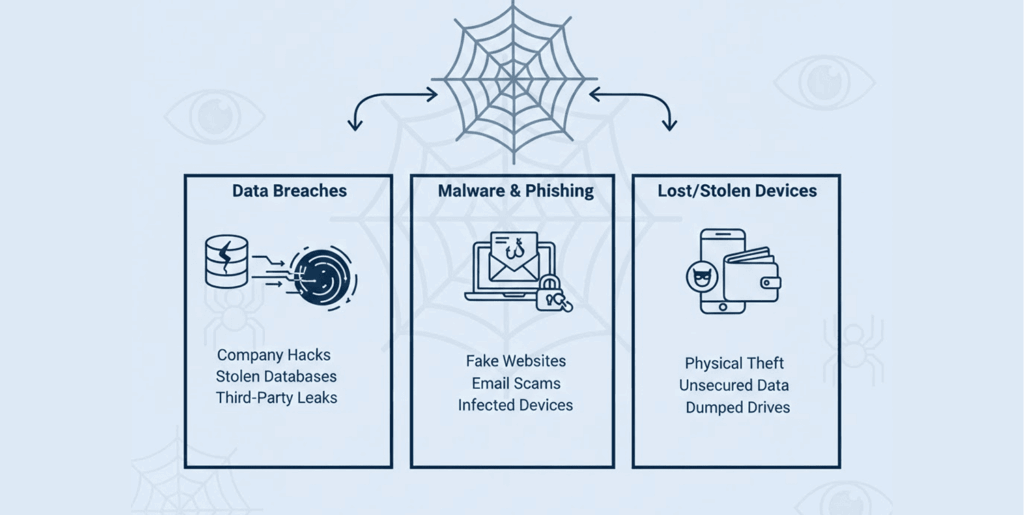
Monitoring services do more than flag stolen data; they trace it back to its origin. By analyzing dark web sources, they reveal how the breach happened and where your information is spreading.
- Third-party breaches: Vendors, cloud services, and partners often hold your data. A breach at your accountant’s firm, your email marketing provider, or a former employer can expose your information. Monitoring for your data catches these indirect leaks.
- Data dumps on hacker forums: Cybercriminals frequently share news of successful attacks with their peers by making a portion (or even all) of a compromised database available for free on popular hacker sites. This is a primary source for services that scan the dark web.
- P2P leaks: Many P2P file-sharing programs allow for accidental sharing of sensitive personal information. Similarly, many storage providers offer free data storage as part of their SaaS (software as a service) offerings, so they can often leave them misconfigured (for example, leaving a bucket of Amazon S3 files public), enabling cybercriminals to collect the exposed records from there.
- Simple accidental leaks: Employees can easily leak sensitive data by sending it to the wrong recipient by email or posting sensitive data to a public repository on GitHub. Attackers can access and exploit the data.
- Brand misuse & impersonations: A Dark Web Monitor allows you to find fake social media accounts, phishing kits, and other kinds of fraud that attempt to use your brand’s logo and name to commit fraud against customers and employees.
- Domain spoofing: Criminals register domains that closely mimic legitimate businesses (like yourcomapanysuport.com vs. yourcompanysupport.com) to use for phishing attacks.
Is Dark Web Monitoring Worth It?
The value proposition differs significantly between individuals and organizations:
Cost-Benefit Assessment for Companies
For businesses, the calculation is often clear. The average cost of a data breach is in the millions of dollars. The return on investment (ROI) associated with your business investing several thousand dollars a year in a monitoring service that can prevent or limit the effects of even one incident is phenomenal. Therefore, it’s a necessary part of doing business in the digital environment today.
What Industry are You in?
Some types of businesses experience more targets than others. Enterprise-level financial, health care, technology, and law firms are at the top of the list as they bear very sensitive data. For them, monitoring is closer to a necessity. Hackers may target a local restaurant for customer payment data, even if its immediate risk seems lower.
The Personal Protection Value
For an individual, the value is more about peace of mind and risk management. If you are a high-net-worth individual, a public figure, or someone who has already been a victim of identity fraud, the service can be invaluable. For the average person, a basic service (often free through a password manager) provides sufficient warning for the most common credential leaks.
Return on Investment (ROI) Perspective
Businesses measure ROI in dollars saved by preventing fraud, lowering incident response costs, and avoiding regulatory fines. Individuals measure ROI in time and stress saved from fraudulent use of their identity, frozen accounts, and damaged credit.
Who Should Monitor for Activity in the Dark Web?
- Any organization, large or small, that stores customer or employee information is vulnerable to misuse.
- Any individual who faces frequent attacks, such as executives, journalists, or activists.
- Anyone wishing to have an early warning system in place for any future exposure of data events that happen to all people living in a modern world, who are willing to take action based on the breach notifications received.
How Does Your Personal Information Get to the Dark Web?
Your data typically arrives through a multi-stage pipeline:
- The breach: The first tier is a compromise of a company or service that you use, with one of their database files stolen.
- Exfiltration: The second tier is copying the stolen data from the victim’s network and transferring it to another location.
- Compilation & sale: The third tier is the combination of this stolen data with other compromised databases, cleaning and formatting it to sell through a Dark Web marketplace or forum. There may be a single buyer or multiple buyers.
- Propagation: After being sold, criminals repackage and resell the data before dumping it publicly on paste sites and forums, where bots scrape it to build massive lists for automated attacks.
What to Do When Your Information Appears on the Dark Web
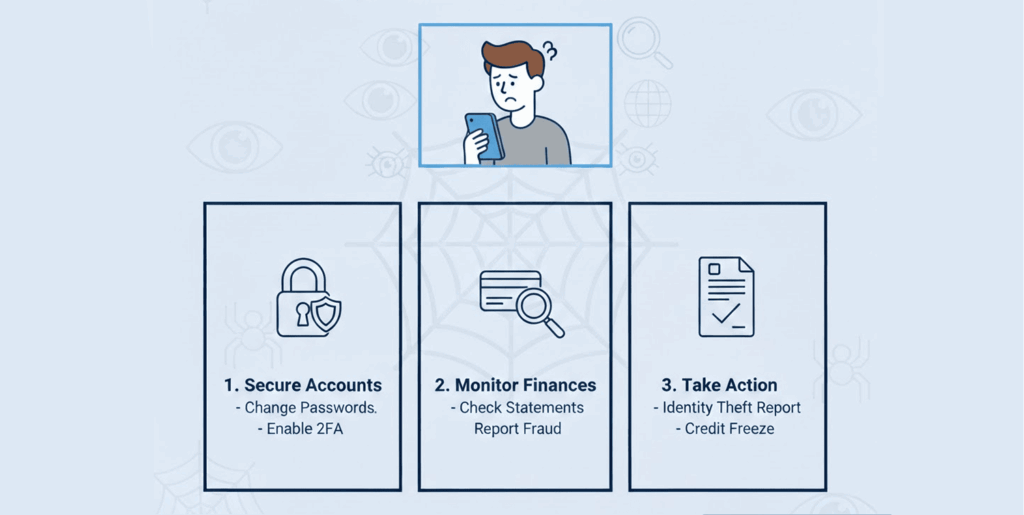
Don’t panic. Instead, act quickly with a possible step-by-step plan:
- Confirm that the alert about your information is from the website that you normally monitor your personal information (do not click on links in emails that you were not expecting).
- Wherever feasible, activate Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) using an application such as Google Authenticator or Authy (not text message if you don’t need to). This makes a stolen password useless on its own.
- For the next 12 months, keep close watch of your financial accounts and your credit files, and ensure you continue to monitor your accounts regularly.
Why Use a VPN for Dark Web Safety
Whether you have a need to conduct your own research or are looking for a way to access the dark web for research-related purposes (like as an investigative-security type of person), having a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is essential to maintaining your privacy while using the Tor Network. A VPN can hide your real IP address from Tor’s entry point and add a level of protection and anonymity to your use of Tor.
This VPN layer operates alongside, not instead of, the Tor network’s own ‘onion routing’ anonymity system. To understand the core anonymizing technology that makes the dark web accessible, our guide on what is onion routing explains the multi-layered encryption process in detail.
Why NordVPN Offers the Strongest Dark Web Protection
When you explore sensitive topics online, the tools that you use for your safety are the most crucial part of your protection plan. Hence, it is important to choose a VPN that provides maximum levels of security, as NordVPN does by offering features specifically intended for the type of user who visits the dark web.
NordVPN not only provides you with IP masking (hiding your internet protocol address), but it also uses many advanced and enterprise-grade technological features that are related directly to the inherent risks associated with the dark web. These multiple features make NordVPN an outstanding choice for dark web protection.
Key features that make a tangible difference for dark web safety:
- Military-grade encryption: NordVPN secures user connections with AES-256-GCM encryption, the global industry standard used by government and commercial organizations. Its NordLynx protocol also employs ChaCha20 encryption to deliver fast and secure performance. Additionally, NordVPN is developing post-quantum encryption to protect users against future threats to today’s encryption standards.
- Obfuscated servers: For dark web access, these features offer key advantages. Onion-over-VPN routes your traffic through NordVPN before entering the Tor network with a single click, adding an extra layer of encryption while simplifying setup. VPN obfuscation further enhances privacy by disguising VPN traffic as normal internet activity, preventing ISPs or observers from detecting VPN use or enforcing restrictions.
- Practical early-warning system: The VPN actively scans the dark web for email addresses linked to your account and sends instant alerts if it finds a match. While you can’t remove stolen data from these sites, early notifications give you time to change passwords or enable multi-factor authentication before your accounts are compromised. This shifts the VPN’s role from a reactive tool to a proactive part of your security strategy.
- Security-first infrastructure: NordVPN uses a secure, modern infrastructure with RAM-only servers that automatically erase all data every time they reboot. Its no-logs policy and security claims are regularly verified through independent audits by trusted firms such as Deloitte and Cure53, ensuring transparency and accountability beyond marketing promises.
- Threat protection: NordVPN’s Threat Protection acts as a pre-filter for your internet traffic, blocking access to known malware and phishing sites commonly linked to dark web threats. It also stops intrusive ad trackers, reducing the risk of accidental malware downloads and unauthorized data exposure.
Conclusion
Dark web monitoring is a legitimate and effective security tool that transforms hidden dark web activity into actionable intelligence. For businesses, it serves as an early-warning system that helps protect assets, meet compliance requirements, and maintain customer trust. For individuals, it offers a critical advantage against identity theft.
However, the real value lies not just in receiving alerts, but in acting on them quickly. Understanding a monitoring service’s capabilities and limits allows users to make informed decisions about integrating it into their overall security strategy.
In an era of constant security incidents involving data, gaining visibility through monitoring is one of the strongest defenses against future data loss and misuse.
FAQs
No. Dark web monitoring and credit monitoring are different. Credit monitoring notifies you after someone tries to open a new credit card in your name, while an underground intelligence gathering service alerts you immediately when your personal data appears on dark websites.
Searching the dark web yourself is risky and not recommended, as it can expose you to malware, phishing, or legal trouble. Professional services offer a safer, automated, and legal way to monitor it.
Once your data appears on the dark web, it’s nearly impossible to remove. Monitoring services warn you immediately, giving guidance to protect or update your sensitive information before further damage occurs.
Choose a transparent monitoring service that clearly explains its methods, limitations, and uses verified alerts. Trusted services have a strong cybersecurity reputation and avoid scare tactics to sell unnecessary services.
If you are using a monitoring service that sends instant email or SMS notifications when a new dark web alert comes out, configure your service accordingly. You shouldn’t have to “check” manually. For free scans, running them every 3-6 months or after news of a major breach is a good practice.